 www.LED
www.LED The PHOTON
If some one is now interested in the "primordial soup", the components of the light, this chapter will give you some answers.
PLEASE NOTE!!!:
Our German sites are much more detailed then our English sites. So please switch in our Germen sites and use the language translater (top right) with 60 languages.
In physics one marks the photon (Greek = light) as the elementary stimulation (quantum) of the quantized electromagnetic field.
More simply expressed photons are the "components" of electromagnetic radiation, also called the "light particles".
One must consider however that all moved (elementary -) particles including the photons has also wave characteristics. This is called: Wave-particle- dualism. But photons are different as elementary particles however by the fact that they have no (probably) proper mass. Mass with speed of light moved by 299.792 km/seconds, would become endless! The experimentally determined and accepted upper mass barrier is with approximately 10-47 kg
That means, the smallest quantity of electromagnetic radiation of arbitrary frequency is
a photon.
Photons have an infinite natural life span, can however with a multiplicity of physical processes be produced or destroyed.
A free photon never is unmovable, but always moves with speed of light.
In optical media the effective speed of light is reduced in the comparison to the vacuum speed of light due to the reciprocal effect of the photons with the subject. Since photons possess energy, they interact in accordance with general relativity theory with the gravitation.
Spin:
Photons are Spin-1 particle and thus bosons. So arbitrarily photons can fill the same quantum-mechanical condition, which is realized for example in a LASER. Photons obtain the electromagnetic reciprocal effect: They are the particles, which permit other particles to interact electromagnetically.

 The electron , first time observed by George Johnstone Stoney 1891, is a negatively charged elementary particle. In the possible experiments electrons show no internal structure and can be accepted to that extent as punctiform. The experimental upper limit for the size of the electron is at present with for instance 10h-19 m.
The electron , first time observed by George Johnstone Stoney 1891, is a negatively charged elementary particle. In the possible experiments electrons show no internal structure and can be accepted to that extent as punctiform. The experimental upper limit for the size of the electron is at present with for instance 10h-19 m.
In atoms and in ions, electrons form the electron sheath. The free mobility of some of the electrons in metals is the cause for the electrical conductivity of metallic leaders.
The Planck constant h is one of the fundamental natural constant of quantum physics! It amounts to: and therefore the dimension of energy has 6.63 x 10h -34Js = 4,136 x 10h -15 eVs times time, thus an effect or an angular momentum.
It arises during the description of quantum phenomena, with which physical characteristics can take not any continuous value, but only certain discrete values.
The Planck constant links particle and wave characteristics, it is the relationship of energy and frequency of a light quantum and the relationship between mass, speed and wavelength any, substantially under-light-fast, particle.
 Bohrschen Atomodel(extended Rutherfordsche model):
Bohrschen Atomodel(extended Rutherfordsche model):
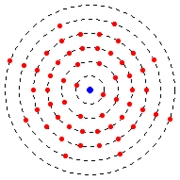
 Electrons move on rugged circular paths around the atomic nucleus.
Electrons move on rugged circular paths around the atomic nucleus.
Differently than the theory of electrodynamics predicts, that the electrons with the circulation, radiates no energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation, i.e. without loss of energy. The larger the distance of the orbit from the core is, the more largely is the energy level of the electron.
The radius of the electron trajectory does not change continuously, but escalately.
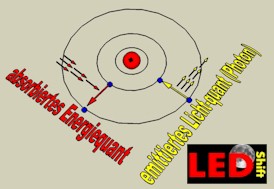
During this quantum jump electromagnetic radiation is emitted (or taken up), whose frequency results from the connection between energy and frequency of light, discovered by Max Planck. This energy is indicated for it in electron volts (eV).
Light emitting semiconductors (LED) must the have the right energy pitch to radiate the desired light frequency, which is bridged with recombination.
Therefor short-wave light (blue or UV) emitting LED must offer a larger energy pitch. After this appropriate semiconductors in history the LED long time was searched.
See chapter semiconductors
| AGB Ledshift | LED Function | LED Producer | LED Distributor | LED Events | LED Company Entry | LEDS | Sitemap | Contact | |
|
|
| © Markus Kottas, Heldenberg Ltd.2018 |